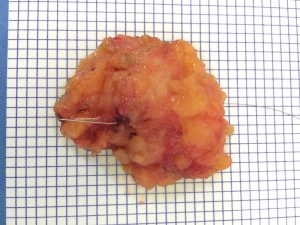
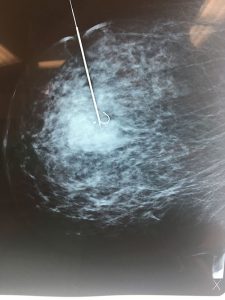
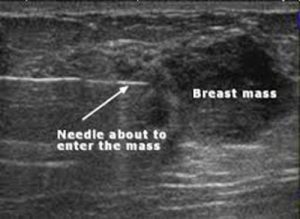
- Factors that increase the number of menstrual cycles: early menarche, nulliparity, & late menopause are associated with an increase risk of breast cancer
- There is no increased breast cancer risk associated with the radiation dose delivered with screening mammography.
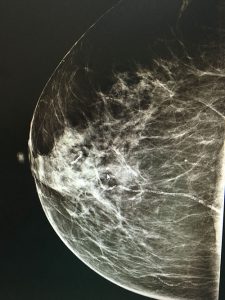
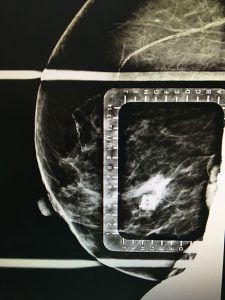
- Screening mammography is used to detect unexpected breast cancer in ASYMPTOMATIC women.
- Breast cancer is the leading cause of death in women ages 40 to 49 years.
- Globally, breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death in women.
- In the United States, breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second most common cause of cancer death in women.
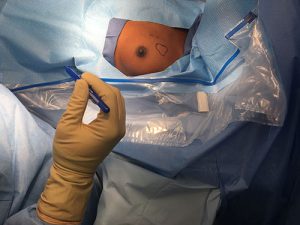
- The goals of Breast-conserving therapy BCT are to provide the survival equivalent of mastectomy, a cosmetically acceptable breast, and a low rate of recurrence in the treated breast.
- For many women with stage-I or II breast cancer, breast conserving therapy BCT is preferable to total mastectomy because BCT produces survival rates equivalent to those after total mastectomy while preserving the breast.
- The surgical approach to the primary tumor depends on the size of the tumor, whether or not multifocal disease is present, and the size of the breast.
- The options include breast-conserving therapy (breast-conserving surgery plus radiation therapy [RT]) or mastectomy (with or without RT). Both approaches result in equivalent cancer-specific outcomes.